The European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) is poised to reshape global trade dynamics, with Asian manufacturing economies facing particularly complex challenges. As the world's factory floor, Asia's export-oriented industries must now grapple with a new layer of compliance that could fundamentally alter their competitive positioning in European markets.
At its core, CBAM represents the EU's bold attempt to level the playing field for domestic producers facing stringent climate regulations. By imposing carbon costs on imports equivalent to those borne by EU manufacturers, the policy effectively extends Europe's carbon pricing regime beyond its borders. For Asian exporters long accustomed to competing on price and scale rather than environmental metrics, this constitutes nothing short of a commercial earthquake.
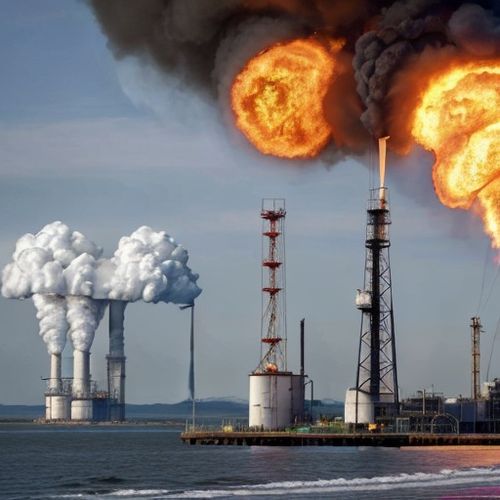
The steel and aluminum sectors appear most vulnerable in the initial phase. Countries like China, India, and South Korea that have built massive export capacities in these energy-intensive industries now face difficult choices. Either invest heavily in decarbonization technologies - with uncertain returns - or accept shrinking margins as carbon costs get priced into their EU-bound shipments. Early estimates suggest CBAM could add 20-35% to current export costs for Asian steelmakers still reliant on coal-fired blast furnaces.
Beyond basic metals, the chemicals and cement industries loom as next in line for CBAM coverage. Here, the geographical concentration becomes even more pronounced. Southeast Asia's emerging chemical hubs and China's world-leading cement production capacity could see their European market access constrained unless they accelerate green transitions. The timeline appears particularly punishing for developing economies, with full CBAM implementation scheduled for 2026 - barely allowing time for major industrial overhauls.
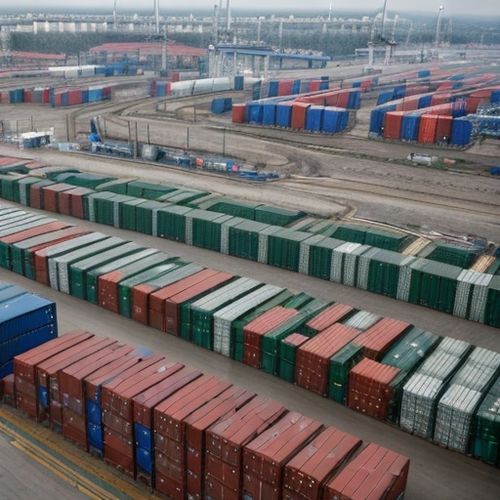
Supply chain complexities present another layer of challenges. Many Asian manufacturers serve as intermediate suppliers to European factories rather than selling finished goods directly. The mechanism's reporting requirements will force unprecedented carbon accounting throughout value chains, potentially giving vertically integrated EU producers an advantage over fragmented Asian supply networks. Small and medium enterprises across Asia's industrial ecosystems may lack the resources to comply with such rigorous documentation demands.
The policy's ripple effects extend beyond direct costs. CBAM effectively creates a new form of trade conditionality, where market access becomes contingent on environmental performance. This could accelerate the bifurcation of global trade into "green" and "brown" streams, with Asian manufacturers needing to develop parallel production systems for different markets. The administrative burden alone could prove prohibitive for all but the largest conglomerates.
Regional disparities in energy infrastructure compound these challenges. While Japan and South Korea have made progress in renewable energy adoption, much of Southeast Asia remains dependent on coal. Vietnam's manufacturing boom, for instance, has been powered largely by coal-fired electricity. CBAM doesn't account for such developmental differences, potentially penalizing late-industrializing economies for energy choices made during their growth phases.
Technology transfer emerges as a critical flashpoint in the CBAM debate. Asian governments argue that climate policies should be accompanied by mechanisms for sharing low-carbon industrial technologies. The current framework offers no such provisions, raising concerns that CBAM could become a protectionist tool disguised as environmental policy. European firms holding patents on key decarbonization technologies may gain competitive advantages that extend far beyond carbon pricing.
Currency dynamics add another dimension to the equation. As Asian manufacturers face CBAM-related cost increases, the potential for currency depreciation to offset these impacts creates perverse incentives. Weaker regional currencies could temporarily boost competitiveness but might trigger inflationary spirals in import-dependent economies. This financial balancing act further complicates strategic planning for export-oriented firms.
The services sector isn't immune from collateral damage. Asia's vast logistics networks, shipping operators, and trade finance institutions must adapt to CBAM's documentation requirements. The mechanism effectively turns carbon accounting into a new form of trade compliance, necessitating upgrades to digital infrastructure and workforce skills across multiple service industries supporting manufacturing exports.
Looking ahead, the most significant impact may be on investment patterns. CBAM creates strong incentives for European firms to reshore production or nearshore to countries with cleaner energy mixes. Asian nations relying on foreign direct investment in manufacturing could see capital flows redirected unless they demonstrate credible decarbonization roadmaps. This investment calculus extends to domestic capital allocation as well, potentially starving traditional industries of modernization funds.
Political responses across Asia reveal starkly different approaches. China has positioned itself as both critic and potential beneficiary, leveraging its growing renewable energy capacity and dominance in solar panel production. India has taken a more confrontational stance, threatening WTO challenges and reciprocal measures. Smaller economies like Thailand and Vietnam find themselves squeezed between development needs and access to critical export markets.
The human dimension of CBAM's impact often gets overlooked. Millions of Asian workers in carbon-intensive industries face uncertain futures as production patterns shift. While the EU promotes its Just Transition framework domestically, no equivalent exists for trading partners. This asymmetry risks creating climate policy winners and losers along geographical lines, potentially fueling protectionist backlashes.
Ultimately, CBAM represents more than a trade policy - it's a forcing mechanism for global industrial transformation. Asian manufacturers that view it solely as a compliance burden risk falling behind. Those approaching it as a catalyst for modernization may discover unexpected opportunities in the emerging low-carbon economy. The coming years will test the region's capacity for industrial adaptation at unprecedented speed and scale.

By Grace Cox/Apr 6, 2025

By Amanda Phillips/Apr 6, 2025

By Michael Brown/Apr 6, 2025
By William Miller/Apr 6, 2025

By Elizabeth Taylor/Apr 6, 2025

By Jessica Lee/Apr 6, 2025

By Olivia Reed/Apr 6, 2025

By Victoria Gonzalez/Apr 6, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Apr 6, 2025

By Emma Thompson/Apr 6, 2025

By William Miller/Apr 6, 2025

By Grace Cox/Apr 6, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Apr 6, 2025

By Jessica Lee/Apr 6, 2025

By Elizabeth Taylor/Apr 6, 2025

By David Anderson/Apr 6, 2025

By Elizabeth Taylor/Apr 6, 2025

By Joshua Howard/Apr 6, 2025

By Daniel Scott/Apr 6, 2025

By John Smith/Apr 6, 2025